Useful git commands
Useful materials for learning git
- This is a website for learning git interactively: https://learngitbranching.js.org/
Data structure used in Git
- The git is an implementation of linked lists
Useful commands
The difference between git merge and git rebase
git mergeandgit rebasecan both combine works from different branches-
While for
git merge, it would create an extra commit, and the commit have two parents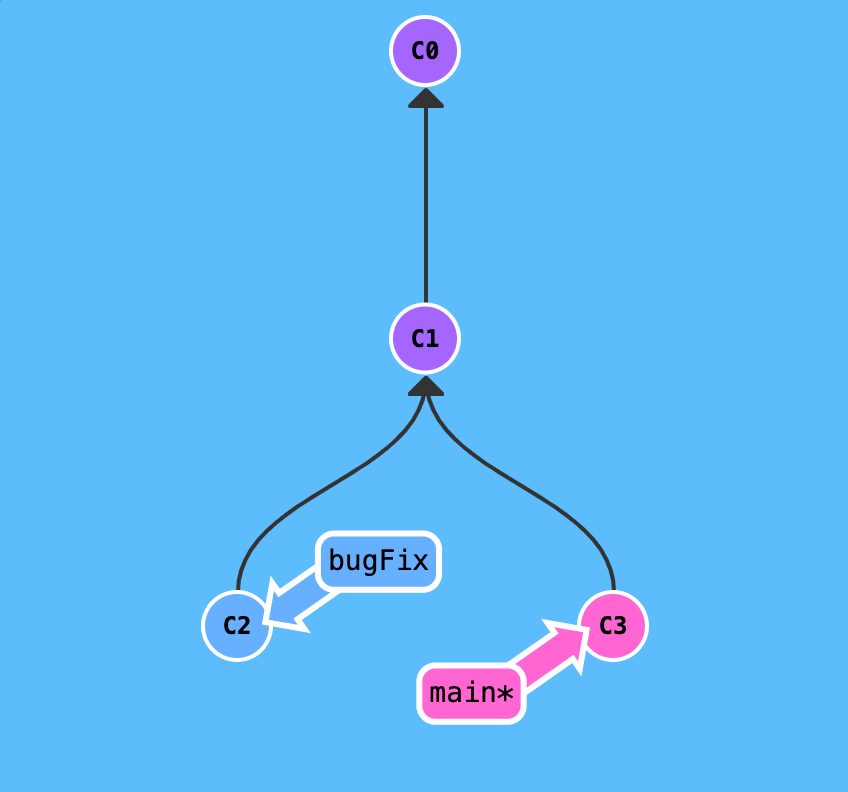
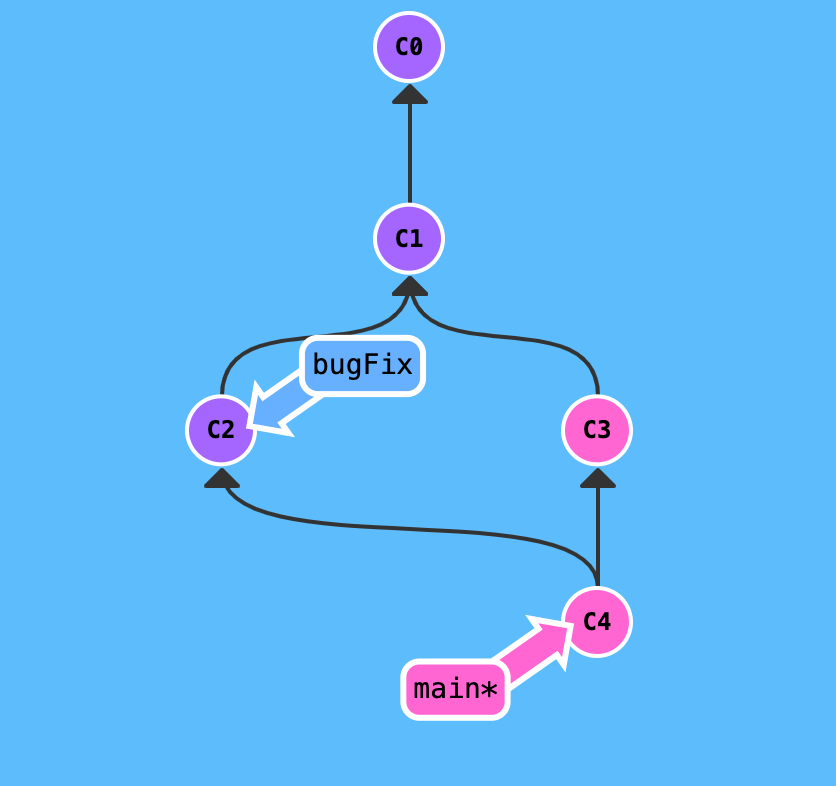
-
git rebasetakes a set of commits, “copies” them, and plop them down somewhere else, the advantage of rebasing is that it can be used to make a nice linear sequence of commits. The commit log / history of the repository will be a lot cleaner if only rebasing is allowed.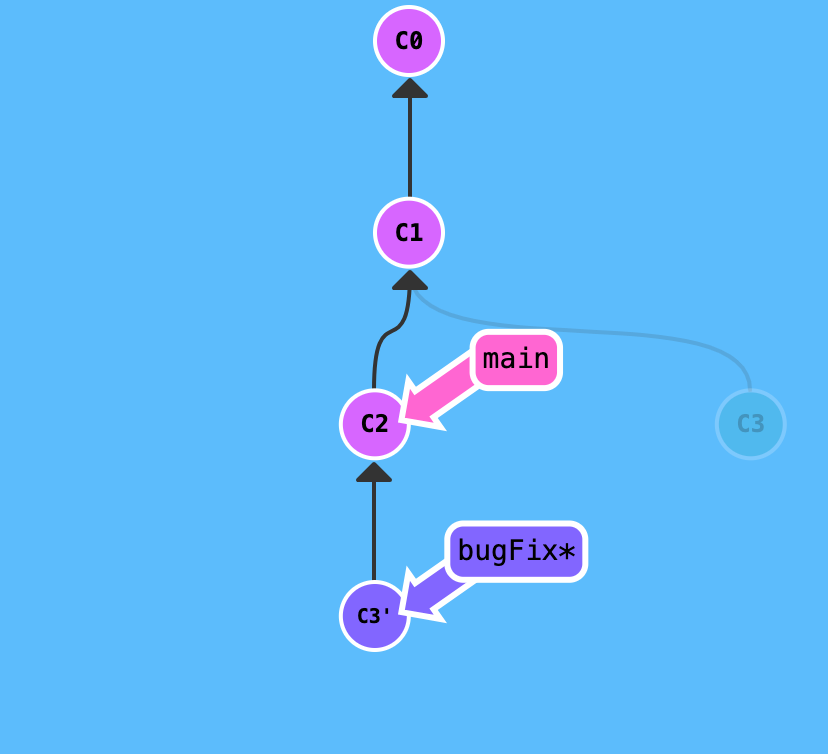
Git submodule
-
Git submodule can manage a separate git repository inside a git repository. It makes the changes easy to track. Below is how to set up git submodules given by ChatGPT:
1. Initialize Your Main Repository: First, create or navigate to the main repository where you want to include the submodule. If you don’t have a repository yet, create one using
git initor clone an existing one usinggit clone.2. Add a Submodule: To add a submodule to your main repository, use the following command:
git submodule add <repository-url> <path-to-submodule>Replace
<repository-url>with the URL of the Git repository you want to include as a submodule and<path-to-submodule>with the desired path within your main repository where the submodule should be located. For example:git submodule add https://github.com/example/repo.git submodules/repo3. Initialize and Update Submodule: After adding the submodule, you need to initialize it and fetch its contents. Use these commands:
git submodule init git submodule updateThe
initcommand initializes the submodule and fetches the submodule’s configuration. Theupdatecommand fetches the submodule’s code.4. Commit the Changes: Now that you’ve added the submodule to your main repository, commit the changes using
git commit. This will record the submodule reference in your main repository.5. Clone or Update a Repository with Submodules: If someone clones your main repository or updates it, they will need to initialize and update the submodules as well. To do this, they can use the following commands:
git clone <main-repo-url> cd <main-repo-directory> git submodule init git submodule updateIf they already have the main repository cloned and want to update the submodules, they can use:
git submodule update --recursive --remote6. Working with Submodules: When you’re working within your main repository, you can navigate into the submodule directory and treat it like a separate Git repository. You can make changes, commit them, and push them from within the submodule directory. However, remember to push changes in the submodule repository separately.
7. Updating Submodules in the Main Repository: If you or someone else makes changes to the submodule, you can update your main repository to include those changes by navigating to the submodule directory and pulling the latest changes. Then, commit the updated submodule reference in the main repository.
8. Removing a Submodule: If you no longer need a submodule, you can remove it from your main repository using the following steps:
- Delete the submodule’s entry in the
.gitmodulesfile. - Remove the submodule directory using
git rm --cached <path-to-submodule>. - Commit the changes.
- Delete the submodule directory from your filesystem.
Using Git submodules allows you to include external code repositories in your project while keeping them separate and manageable. However, they can be a bit complex, so make sure to read the Git documentation for further details and advanced use cases.
- Delete the submodule’s entry in the
Git cherry-pick
By using git cherry-pick <commitHash> can apply a specified commit on the desired branch.
Questions and answers
- Sometimes, I just want to ignore specific files for myself, and I don’t want to share them with collaborators by
.gitignore, what can I do?- https://luisdalmolin.dev/blog/ignoring-files-in-git-without-gitignore/